Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
MCQsHaloalkanes are derivatives of hydrocarbon in which hydrogen atom is replaced by halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, I). We can also say that the compounds containing a halogen atom bonded to a saturated (sp3) carbon are haloalkanes. Haloalkanes are also called alkyl halide as halide is directly attached to alkyl group.
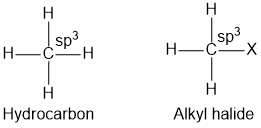
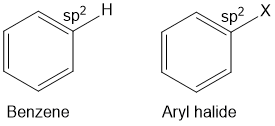
Haloarenes are derivatives of benzene in which hydrogen atom is replaced by halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, I). In haloarenes, the halogen atom is bonded to unsaturated (sp2) carbon. Haloalkanes are also called aryl halide as halide is directly attached to aryl group. Haloalkanes and haloarenes does not occur in nature and they are synthesized in the laboratory.
Read Hybridization and its Exceptions
Classification of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
On the Basis of Number of Halogen Atoms
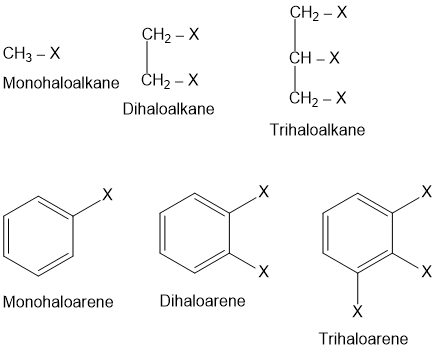
These may be classified as mono, di, or poly halogen (tri-, tetra-, etc.) compounds depending on whether they contain one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Mono halo compounds may further be classified according to the hybridisation of the carbon atom to which the halogen is bonded, as discussed below-
Compounds Containing sp3 C—X Bond (X = F, Cl, Br, I)
Halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group (R). They form a homologous series represented by CnH2n+1X. They are further classified as primary, secondary or tertiary according to the nature of carbon to which halogen is attached.
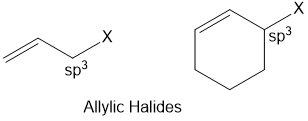
Allylic halides
Halogen atom is bonded to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom next to carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) i.e. to an allylic carbon.
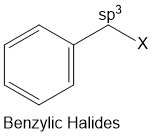
Benzylic halides
Halogen atom is bonded to an sp3-hybridised carbon atom next to an aromatic ring.
Compounds Containing sp2 C—X Bond
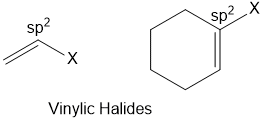
Vinylic halides
Halogen atom is bonded to an sp2-hybridised carbon atom of a carbon-carbon double bond (C = C).
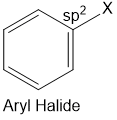
Aryl halides
Halogen atom is bonded to the sp2 -hybridised carbon atom of an aromatic ring.
Nomenclature
Nomenclature of Haloalkanes
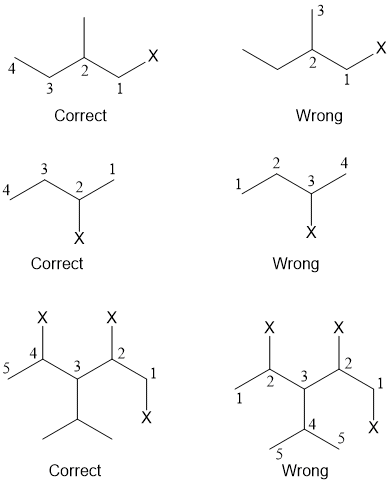
The following rules are used for naming haloalkanes according to the IUPAC system.
1. The longest chain of the carbon atoms bearing the halogen atom is selected.
2. Numbering of the carbon atoms in the chain is done in such a way that the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom gets the lowest number.
3. The word chloro, is prefixed to the parent hydrocarbon name.
4. In case of alkyl substituted haloalkanes, the longest chain containing halogen atom is selected for numbering.
5. When two or more halogen atoms are present in a compound, the longest chain selected must contain the maximum number of halogen atoms. The multiplicative prefixes (di, tri, tetra, etc.) are added before the name of halogen atom to indicate the number of halogen atoms.
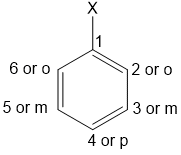
Nomenclature of Haloarenes
In naming a haloarene, the prefix chloro, bromo-or iodo- etc. is are added to name of arene according to halogen(s) present. The relative positions of halogen atoms are indicated by appropriate numbers. The prefixes ortho (o-), meta(m-) and para (p-) are also commonly used respectively to indicate the relative positions i.e. 1,2- ;1,3 − and 1,4- of substituents in a benzene ring.
Nature of C-X Bonds
Halogens are more electronegative than carbon. Thus, the electron density along the C–X bond is displaced in the direction of the halogen. Thus, the C–X bond in polar in nature. The carbon atom bears a partial positive charge (δ+) and the halogen atoms bears a partial negative charge (δ–). Depending upon the type of halogen attached to the haloalkanes, the partial charge on C–X bond and the polarity may differ.
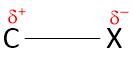
Haloarenes have the halogens bonded to sp2 hybridized carbon of the benzene ring. The C–X bond is polar, too, as in haloalkanes. However, the difference between the C–X bond in haloalkanes and haloarenes is that the C–X bond acquires a partial double bond character because the partial charge on the halogens is involved in resonance with the ring. Hence, the polarity of the C–X bond in haloarenes is lesser than the haloalkanes, and the bond length of the C–X is also shorter than the haloalkanes.
Read in details Nature of C-X Bonds in Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Optical Rotation in Haloalkanes
When a plane-polarized light passes through a solution of chiral compound, it can rotate the polarized light either to the right or clockwise direction called dextrorotatory (a Greek word which means right rotation) and is indicated by "+" or to the left or anticlockwise direction called levorotatory (a Greek word which means left rotation) and is indicated by "-"). The angle by which the plane polarized light is rotated is called the optical rotation.
Optical rotation is measured using a device called a polarimeter. The sample of the chiral compound is placed in a tube, and plane-polarized light is passed through it. The angle of rotation is measured and recorded. The degree of rotation is determined by the concentration of the enantiomer in solution, the length of the sample tube, and the wavelength of the light used. Optical rotation is a function of time and it is used to determine kinetic reactions.

Example: 2-bromobutane
2-bromobutane has one assymetric carbon showing two optical isomers (enantiomers). Each enantiomer will rotate plane-polarized light by a specific angle. One enantiomer will rotate it to the right, and the other to the left.

Also read Optical Isomerism
Physical Properties of Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes are usually colorless, but bromides and iodides can develop color when exposed to light.
Lower haloalkanes are gases, while higher haloalkanes are liquids or solids.
The melting and boiling points increase with increase in size due to higher vander waal's forces. Hence the order is:
R−I > R−Br > R−Cl > R−F
The boiling points of isomeric haloalkanes decrease with increase in branching as surface area decreases on branching and Vander waal's forces decrease
CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl > (CH3)2CHCH2Cl > (CH3)3CCl
The boiling points of isomeric dihalobenzene are nearly the same.
The melting point of p-dihalobenzene is always higher than those of the o- and p- isomers. Because p-isomers are more symmetrical and hence their molecules pack closely in the crystal lattice. This leads to stronger molecular forces of attraction.
Haloalkanes though polar, are immiscible with water because they neither form H-bond nor break the already existing H-bonds (because new attraction of water and haloalkanes is weaker).
Haloalkanes are soluble in organic solvents of low polarity like ether, benzene etc., because new intermolecular forces are similar to those in the low polarity solvents.
Alkyl fluorides and alkyl chlorides are generally lighter than water whereas alkyl bromides and alkyl iodides are heavier. The relative densities follow the order:
RI > RBr > RCl.
The densities of the alkyl halides decreases as the size of the alkyl group increases.
The stability of the haloalkanes having the same alkyl group decreases in the order:
R−F > R−Cl > R−Br > R−I
since the strength of the C−X bond decreases in the order:
C−F > C−Cl > C−Br > C−I
The Dipole moment decreases as the electronegativity of the halogen decreases. The dipole moment of methyl halides follows the order:
CH3Cl > CH3F > CH3Br > CH3I.
Due to the very small size of F, fluorides have lower dipole moments than chlorides.
Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes
From Alcohol
The hydroxyl group of an alcohol is replaced by halogen on reaction with concentrated halogen acids, phosphorus halides or thionyl chloride. Thionyl chloride is preferred because in this reaction alkyl halide is formed along with gases SO2 and HCl. The two gaseous products are escapable, hence, the reaction gives pure alkyl halides. The reactions of primary and secondary alcohols with HCl require the presence of a catalyst, ZnCl2. With tertiary alcohols, the reaction is conducted by simply shaking the alcohol with concentrated HCl at room temperature.

From Alkanes
Free radical chlorination or bromination of alkanes gives a complex mixture of isomeric mono- and polyhaloalkanes, which is difficult to separate as pure compounds. Consequently, the yield of any single compound is low.


IIT-JEE(Main) Shift-1 Date:22.1.2025
Secondary butyl cyclohexane when reacts with Br2 in presence of sunlight produce
Solution:


IIT-JEE(Main) Shift-1 Date:23.1.2025
How many dichlorinated products can be obtained for n-propane?
Solution:
Five dichlorinated products can be obtained from n-propane.

From Alkenes
An alkene is converted to corresponding alkyl halide by reaction with hydrogen chloride, hydrogen bromide or hydrogen iodide. Unssymetrical alkenes yields two products, however only one predominates as per Markovnikov’s rule.

Finkelstein Reaction
Alkyl iodides are often prepared by the reaction of alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides with NaI in dry acetone. This reaction is known as Finkelstein reaction.
R−X + NaI → R−I + NaX
Swart Reaction
Alkyl fluoride can be prepared by heating alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2 or SbF3. This reaction is known as Swart reaction.
R−X + AgF → R−F + AgX
Preparation of Haloarenes
From Hydrocarbons by Electrophilic Substitution

From Amines by Sandmeyer's Reaction
When a primary aromatic amine, dissolved or suspended in cold aqueous mineral acid, is treated with sodium nitrite, a diazonium salt is formed. Mixing the solution of freshly prepared diazonium salt with cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide results in the replacement of the diazonium group by –Cl or –Br.

Replacement of the diazonium group by iodine does not require the presence of cuprous halide and is done simply by shaking the diazonium salt with potassium iodide.

Chemical Properties of Haloalkanes
Important Nucleophilic Substitution Raections


IIT-JEE(Main) Shift-2 Date:29.1.2025

Solution:


IIT-JEE(Main) Shift-2 Date:24.1.2025

Solution:

Elimination Reactions
Haloalkanes can undergo elimination reactions when treated with alcoholic KOH or alcoholic NaOH, resulting in the formation of alkenes.
CH3−CH2−X → CH2=CH2
read elimination reaction
Wurtz Reaction
When alkyl halides are treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, higher alkanes are formed. If a mixture of two different alkyl halides is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, a mixture of alkanes is obtained. Self-coupling products are formed in preference to cross-coupling products.
Reaction with Magnesium Metal or Formation of Grignard Reagent
When an alkyl halide is treated with pure and dry magnesium in the presence of pure and dry ether, an alkyl magnesium halide known as a Grignard reagent is formed. This reagent is used in the preparation of a large number of organic compounds.

IIT-JEE(Main) Shift-2 Date:22.1.2025
How many R – Br can form isopentane?

Solution:
 Total four R–Br can form isopentane in this reaction.
Total four R–Br can form isopentane in this reaction.
Chemical Properties of Haloarenes
Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
Haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions of the benzene ring such as halogenation, nitration, sulphonation and Friedel-Crafts reactions. Ortho and Para substituted products are formd but para product is major.

Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol by heating in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623K and a pressure of 300 atmospheres. This is known as Dow's method.

Fittig Reaction
Aryl halides react with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to give diphenyl. This reaction is called Fittig reaction
Wurtz-Fittig Reaction
When aryl halides react with alkyl halides and sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to give substituted aromatic compounds. This is called Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Some Useful Poly Halogen Compounds
Large number of polyhalogen aliphatic and aromatic halogen compounds are known. These are extensively used as solvents, pesticides, anaesthetics etc. Some important compounds are chloroform (CHCl3), iodoform (CHI3), carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), benzene hexachloride (BHC), DDT, etc.
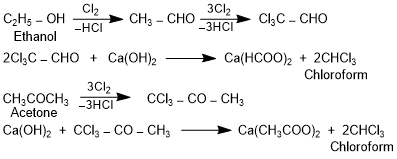
Chloroform (CHCl3)
Chlorofom is a derivative of the simplest hydrocarbon, methane. Its IUPAC name is trichloromethane. Chlorofom is prepared in the laboratory by treating ethanol or propanone with chlorine gas in the presence of an alkali. Chlorofom is a colourless sweet smelling liquid (b.p. 334K). CHCl3 is slowly oxidized by air in the presence of light to a poisonous gas, phosgene. Therefore, chloroform is stored in dark coloured bottles to protect it from light. Chloroform is used in isocyanide test for the detection of primary amines.
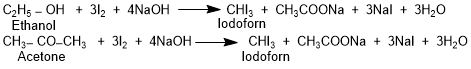
Iodoform (CHI3)
Iodoform is a pale yellow solid with a distinct smell. Its IUPAC name is triiodomethane. Iodoform is prepared by heating ethanol or acetone with iodine in the presence of alkali. Yellow crystals of iodoform can easily be recognized by the characteristic smell. Formation of iodoform is used to test compounds containing methyl ketone and secondary alcohol.
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)
DDT is available in powder, aerosols, granules etc. forms. DDT is used mainly to control mosquito-borne malaria. It is also used as an argicultural insecticide. The use of DDT has been banned in many countries because being non-biodegradable, it accumulates in environment. It is toxic to other living organisms such as: mammals, birds, fishes, etc.
Some halogen containing compounds are useful in daily life. Some compounds of this class are responsible for exposure of flora and fauna to more and more of UV light which causes destruction to a great extent. Name the class of these halocompounds. In your opinion, what should be done to minimise harmful effects of these compounds.
Some halogen containing compounds are useful in daily life are as follows
Dichloromethane It is used as a solvent as a paint remover, as a propellant in aerosols, and as a process solvent in the manufacture of drugs. It is also used as a metal cleaning and finishing solvent.
Trichloromethane It is employed as a solvent for fats, alkaloids, iodine and other substances.
Triodomethane It is used as an antiseptic. Now, it has been replaced by some other compounds because of its objectionable smell. But some compounds of this class are responsible for exposure of flora and fauna to more and more of UV light which causes destruction to great extent. These are as follows-
Tetrachloromethane When carbon tetrachloride is released into the air, it rises to the atmosphere and depletes the ozone layer. Depletion of the ozone layer is believed to increase human exposure to UV rays leading to increased skin cancer, eye diseases and disorders, and possible disruption of the immune system. These UV rays cause damage to plants, and reduction of plankton populations in the ocean's photic zone.
Freons Freon-113 is likely to remain in the air long enough to reach the upper atomsphere. Here, it provides chlorine atoms which damage the ozone layer. Because of this depletion UV rays enters in our atmosphere and become responsible for damage to great extent.
p p'-Dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethane (DDT) DDT is not completely biodegradable. Instead, it gets deposited in fatty tissues. If ingestion continues for a long time, DDT builds up within the animal and effect the reproductive system.
To minimise the harmful impacts of these compounds i.e., freons, hydrofluorocarbons, fluorocarbons and hydrocarbons can be straight used to make refrigerants and air-conditioning equipments. They are stable in the stratosphere and secure for flora and fauna.
Questions-Answer of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution. Although both carbon and nitrogen atoms are in a position to donate electron pairs, the attack takes place mainly through carbon atom and not through nitrogen atom since C—C bond is more stable than C—N bond. However, AgCN is mainly covalent in nature and nitrogen is free to donate electron pair forming isocyanide as the main product
Sulfuric acid is a strong acid as well as strong oxidizing agent. So, it oxidizes the hydrogen iodide produced in the reaction to iodine molecule. This prevents the reaction between alcohol and hydrogen iodide to produce alkyl iodide.
2KI + H2SO4 → 2KHSO4 + 2HI
2HI + H2SO4 → 2H2O + I2 + SO2
To overcome this problem, phosphoric acid is used which provides HI for the reaction to produce alkyl iodide.

The melting point of p-dibromobenzene is higher than that of o- and m- dibromobenzene. This is due to the symmetry of p-dibromobenzene, which allows the molecule to fit into the crystal lattice more easily. As a result, breaking the bonds between the molecules requires a higher temperature, resulting in a higher melting point. The order of their melting point is
m-Dichlorobenzene < o-Dichlorobenzene < p-Dichlorobenzene
In aqueous KOH, OH– acts as nucleophile which replaces another nucleophile.
R-X + (aq)KOH → R-OH + KX
Where as in alcoholic KOH, C2H5O– ion is produced which is a strong base hence β-elimination took place to form alkene.
C2H5OH + KOH → C2H5O– + K+
C2H5X + (alc)KOH → C2H5OH + KX
Grignard reagent react with water to form alkanes, that's why they are prepared under anhydrous condition.
Alkyl fluoride can be prepared by heating alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2 or SbF3. This reaction is known as Swart reaction. The reaction is as follows:
CH3–Br + AgF → CH3F + AgBr
When alkyl halides come in contact with sodium metal in a dry ethereal (moisture-free) solution form higher alkanes. It can also be applied to produce higher alkanes with an equal number of carbon atoms. By this method methane can not be prepared. The reaction is as follows:
2R–X + 2Na ⟶ R–R + 2NaX
The formula C3H7Cl depicts that compound (A) is an alkyl halide. Compound (B) is formed when there is a reaction with KCN. When compound (C) is reduced with hydrogen and nickel it produces 1-aminobutane that concludes that all the compounds mentioned above in the question are straight-chain compounds. Therefore, compound (A) is a 1-Chloropropane, compound (B) is a Propionitrile, and compound (C) is a Butanamide.
A. Boiling points generally increase with molecular weight and the presence of heavier halogens. Chloromethane < Bromomethane < Dibromomethane < Bromoform
B. The boiling point increases with molecular size and chain length, while branching tends to decrease boiling points.
Isopropyl chloride < 1-Chloropropane < 1-Chlorobutane
Electron pairs of Cl atom are in conjugation with electrons of the benzene ring so C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene acquires some double bond character while C-Cl bond in cyclohexyl chloride. Since dipole moment is a product of charge and distance, so chlorobenzene has lower dipole moment than cyclohexyl chloride.
B. Alkyl halides are polar molecules, therefore, their molecules are held together by dipole-dipole attraction. The molecules of H2O are held together by H-bonds. Since the new forces of attraction between water and alkyl halide molecules are weaker than the forces of attraction already existing between alkyl halide-alkyl halide molecules and water-water molecules, therefore, alkyl halides are immiscible with water.
C. Grignard's reagents are very reactive. They react with alcohol, water, amines etc. to form corresponding hydrocarbon.
R-MgX + HOH → RH + Mg(OH)X
Therefore, Grignard's reagents must be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
A. n-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than t-butyl bromide because it has larger surface area hence have more Van der Waals' forces.
B. Rotation due to one enantiomer is cancelled by another enantiomer.
C. The presence of nitro group (-NO2) at ortho and para positions withdraws the electron density from benzene ring and thus facilitating the attack of nucleophile out.
Dialkyl lithium cuprate (R2CuLi) reacts with alkyl halide to give alkane. This reaction is known as Corey-House reaction. This is a better method than the Wurtz reaction for the preparation of alkanes because, it can be used for preparing symmetrical, unsymmetrical, straight chain, or branched chain alkanes.
R-X + R2-CuLi → R-R + R-Cu + LiX
Chloroalkanes are conveniently prepared by refluxing alcohol with thionyl chloride (SOCl2) in presence of pyridine (C5H5N).
R — OH + SOCl2 → R — Cl + SO2↑ + HCl↑
Alkyl chlorides react with AgNO3 to give white precipitate which is soluble in alcoholic ammonium hydroxide.
Alkyl bromides react with AgNO3 to give a yellow precipitate which is sparingly soluble in alcoholic ammonium hydroxide.
Alkyl iodides react with AgNO3 to give dirty yellow precipitate, which is insoluble in alcoholic ammonium hydroxide.
Vinyl and aryl halides do not yield silver halide under these conditions.
Allyl chloride undergoes ionization readily to produce resonance stabilized allyl carbocation. Allyl carbocation being reactive in nature combines with OH− ions to give allyl alcohol. On the other hand, n-propyl chloride does not undergo ionization to produce n-propyl carbocation. Hence, allyl chloride is hydrolyzed more readily than n-propyl chloride.
The molecular formula C5H10 suggests that it is either a cycloalkane or an alkene.
Given that it doesn't react with chlorine in the dark, so it can not be alkenes because alkenes are generally react with chlorine even without light.
Since the hydrocarbon gives only one monochloro compound, it indicates that all the hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon are equivalent. Thus, the compound is cyclopentane.

Primary alkyl halide with the formula C4H9Br may be either n-butyl bromide (1-bromobutane) or isobutyl bromide (2-methyl-1-bromopropane).
compound (a) must be isobutyl bromide.

Aqueous KOH contains only OH– ions, which acts as nucleophile and these bring about hydrolysis of alkyl chlorides to the corresponding alcohol.
R–CH2–CH2–X + aq. KOH → R–CH2–CH2–OH + KX
On the other hand, alcoholic KOH contains ethoxide ions (C2H5O–), which are more basic than OH– ions. Consequently, the ethoxide ions favoring dehydrohalogenation to form the alkene.
R–CH2–CH2–X + alc. KOH → R–CH=CH2 + HX
Download Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT PDF | Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class 12 MCQs, Short Questions and Long Questions with Answer for Board Exams, NEET and IIT-JEE
