What are Electrical double layer and zeta potential? Discuss the factors which affects the Formation of Electrical Double Layer.
Electrical double layer
Electrical double layer is the region near a charged surface where potential difference exists due to the presence of ions. It consists of two layers, the inner Helmholtz layer and the outer Helmholtz layer. The layer of ions attracted to the charged surface, which creates an electric field is inner Helmholtz layer, and the outer Helmholtz layer is a layer of ions attracted to the inner Helmholtz layer, forming a counter-charge layer.
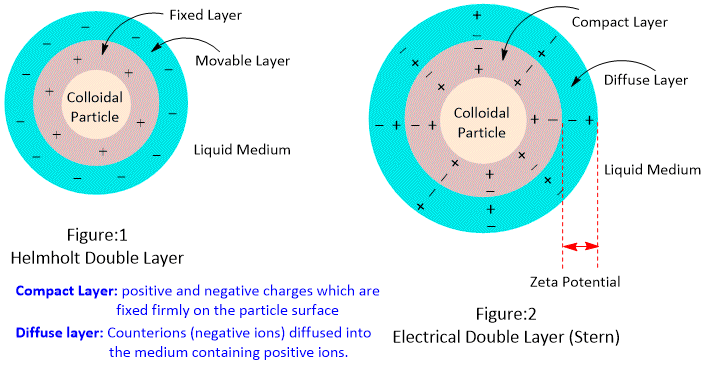
Formation of the electrical double layer can be explained by the Gouy-Chapman-Stern theory (GCS Theory), which states that when a charged surface is immersed into an electrolyte solution, ions from this solution will be attracted towards this surface and will produce an ionic compact layer on it. This layer of ions is pushed back by the repulsive forces between ions, creating a diffuse layer. The combination of both compact and diffuse parts forms Stern Double Layer also called Electrical Double Layer.
The thickness of this layer depends on various factors such as ionic strength of the solution, surface charge density and size of its ions. The diffused double-layer thickness (d) was calculated by Gouy using Debye-Huckel theory in 1909.
Zeta Potential
Zeta potential is the potential difference between the surface of the charged particle and the surrounding fluid. It is an important parameter to measure the surface charge of colloidal particles and is also used to predict the stability and behavior of colloidal systems. The zeta potential is affected by factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of other ions in the solution.
Keeping the total concentration of the electrolyte constant, increases the amount of electrolytes or increasing the valency of the counter ions, decreases the Stern and Zeta potentials owing to the decrease in thickness of the double layer. Zeta potential acts as an energy barrier for the stability of colloids and suspensions.
Zeta potential determines the degree of repulsion between adjacent, similarly charged dispersed particles and therefore, has practical applications in the stability of systems containing dispersed particles.
Zeta potential cannot be measured directly. It can be measured by using techniques like electrophoresis, where an electric field is applied to the charged particles, and their movement is recorded. The magnitude and direction of the particle's movement can give valuable information about the zeta potential and surface charge.
Factors Influencing Electrical Double Layer Formation
The formation of an electrical double layer is a complex and dynamic process that is influenced by several factors. These factors play a crucial role in determining the properties and behavior of the double layer. Some important factors that influence the formation of the electrical double layer are discussed below-
- Charge Density of the Surface : The charge density of the solid surface is the primary factor that determines the formation of an electrical double layer. A higher charge density of the surface, stronger the interaction with the ions in the solution, leading to a thicker and more stable double layer because a higher charge density creates a larger electric field which in turn, attracts more ions to the surface.
- Electrolyte Concentration : Higher concentration of electrolyte, increases the number of ions in the solution makes a thinner double layer because the excess ions in the solution are attracted to the surface, forming a dense and compact layer.
- Charge of the Ions : Higher the charge on ions, stronger the interaction with the surface and creates a thicker and more stable double layer. This follows the Schulze-Hardy rule.
- Nature of the Solid Surface and Adsorbed Species : The material composition, roughness, and presence of adsorbed molecules all affect the surface charge and the binding affinity for ions.
- Temperature : Increases the temperature, increases the mobility of ions, leading to a thicker and more diffuse (less compact) double layer.
Temperature also affects the viscosity of the solution, which changes the thickness of the double layer. - pH of the Solution : For ionizable surfaces, pH dictates the degree of protonation/deprotonation, controlling the surface charge and, consequently, the electric double layer thickness (minimized at the isoelectric point).
Electrical double layer and zeta potential MCQs
Correct statement about Helmholtz electrical double layer is
I. It is a combination of two layer of similar charges around colloidal sol.
II. It is a combination of two layers of opposite charges around the colloidal sol.
III. In it 1st layer of ions is diffused while 2nd layer of ions is fixed.
IV. The potential difference the fixed layer and the diffused layer is called zeta potential.
B. I and III
C. II and IV ✔
D. III and IV
Zeta potential (or electrokinetic potential) is the
A. potential required to bring about coagulation of a colloidal solB. potential required to give the particles a speed of 1 cm/s in the sol
C. potential difference between fixed charged layer and the diffused layer having opposite charge ✔
D. potential energy of the colloidal particles
Measuring Zeta potential is useful in determining which property of colloidal solution?
A. Stability of the colloidal particles ✔B. Size of the colloidal particles
C. Viscosity
D. Solubility
