Vapour Pressure Curves for Non-ideal Solution or
Raoult's law curves of Non-ideal Solutions
In case of non ideal solutions, the vapour pressure curve is not a straight line. Suppose the molecules of the solvent and solute are represented by A and B respectively. Now let γAB be the attractive force between A and B and γAA between A and A.
If γAB = γAA then the vapour pressure is not deviate from that of ideal solution(predicted by Raoult's law). However, if
γAB > γAA
molecule A will escape less readily and the vapour pressure will be less than that predicted by Raoult's law (Negative deviation). On the other hand, if
γAB < γAA
A molecule will escape from the solution surface more readily and the vapour pressure of the solution will be higher than predicted by Raoult's law (Positive deviation).
In very dilute solutions of nonelectrolytes, the solvent and solute molecules are very much alike in both molecular size and molecular attractions. Thus such solutions tend to approach the ideal behaviour and obey Raoult's law fairly accurately.
Vapour Pressure Curves of Solutions Showing Positive Deviation
If the molecular interactions between A and B are weaker than the A-A or B-B molecular interactions, then the escaping tendency of the molecules of A and B from the solution becomes more than that from the pure liquids. Consequently, the vapour pressure of the solution will be greater than that of an ideal solution of the same composition. Such solutions are said to show positive deviation from Raoult's law.
Mathematically,
PA = PoA XA
PB = PoB XB
P > PoA XA + PoB XB
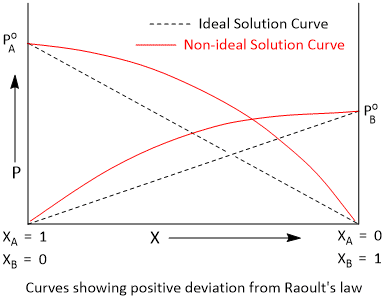
In ethanol, there is a strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding. When cyclohexane is added to it, the cyclohexane molecules get in between the ethanol molecules; thereby decreasing the intermolecular interactions. During the formation of such solutions, heat is absorbed and there is a slight increase in volume. These solution show small positive deviation. However, when water or chloroform is added to ethanol a large positive derivation shows because of weaker intermolecular interactions.
Vapour Pressure Curves of Solutions Showing Negative Deviation
If the intermolecular forces between A and B are stronger than those of A-A and B-B, the solution formed by mixing A and B shows negative deviation from Raoult's law. Due to stronger A-B interactions, the escaping tendency of A and B from the solution becomes less than that from the pure liquids. The vapour pressure of such as a solution will be less than an ideal solution of the same composition.
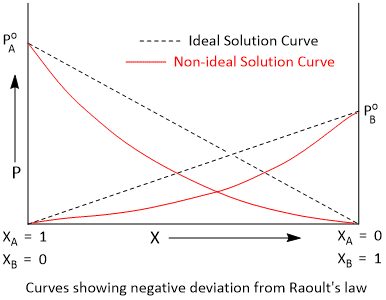
When acetone and chloroform are mixed, they form hydrogen bonds with each other. Consequently, the intermolecular attractions between acetone and chloroform become stronger. The tendency of the molecules to escape from the solution, thus, decreases. The vapour pressure, therefore, decreases and shows negative deviation from Raoult's law. During the formation of such solution, heat is evolved and there is slight decrease in volume.
Which of the following is not an example of a non-ideal solution showing negative deviation?
A. HNO3 + WaterB. HCl + Water
C. Acetic acid + Pyridine
D. Carbon tetrachloride + Toluene ✔
Which of the following is an example of a non-ideal solution showing positive deviation?
A. Acetone + Carbon disulphide ✔B. Chlorobenzene + Bromobenzene
C. Chloroform + Benzene
D. Acetone + Aniline
Water and ethanol form non-ideal solution with positive deviation from Raoult's law. This solution will have vapour pressure
A. equal to vapour pressure of pure waterB. less than vapour pressure of pure water
C. more than vapour pressure of pure water ✔
D. less than vapour pressure of pure ethanol
