Synthesis of Chloramphenicol or Chloromycetin
Structure of Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is a levorotatory broadspectrum naturally synthesized antibiotic. It is naturally biosynthesized by bacteria in the genus Streptomyces (particularly Streptomyces venezuelae). Chloramphenicol was first isolated in 1947 from a soil sample in Venezuela. It is primarily synthesized by S. venezuelae. However, chloramphenicol is now synthesized by chemical processes in which the nitrobenzene ring of the antibiotic is chemically modified.
Long et al (1949) Synthesis
Synthesis of Chloramphenicol or Chloromycetin from p-Nitroacetophenone
Chloramphenicol is useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. It is used to treat conjunctivitis, blepharitis, meningitis, plague, cholera, and typhoid fever.
The number of chiral carbon in Chloromycetin is
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Zero
Answer: B. Two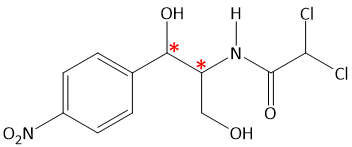
There are two chiral carbon atoms in Chloramphenicol or Chloromycetin shown by asterisk(*) mark.
