Bragg's Equation
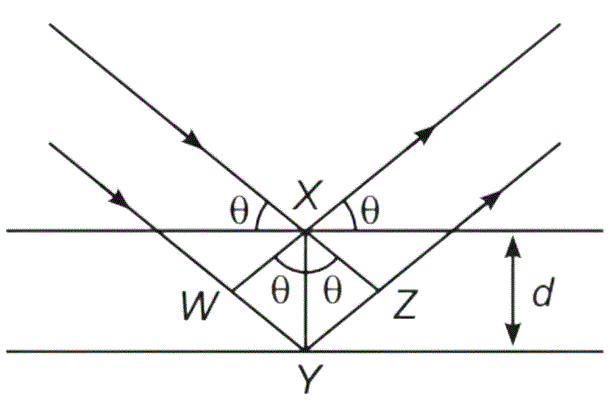
Thus, Path difference = WY + YZ
= XY sinθ + XY sinθ
= 2XY sinθ
= 2d sinθ
So, nλ = 2d sinθ
This equation is Known as Bragg's equation.
where, n = 1,2,3...(diffrection order)
λ = wavelength of X-rays
d = distance between planes
θ = angle at which interference occurs.
How to Utilize Bragg's Equation to Determine Crystal Structure
The X-ray diffraction processes used for crystals are of two types-the rotating crystal process and powder process. In the latter, a powdered sample is used in place of crystal and hence simple exposure of X-rays is sufficient and so no rotation is necessary because powdered sample has crystals arranged in all possible orientations.In rotating crystal process, a narrow beam of X-ray strikes a crystal mounted on the turn table. The crystal is rotated so as to increase glancing angle at which the X-rays are incident at the exposed face of the crystal. The intensities of the reflected rays are measured on the recording device. The angle of the maximum reflections is θ of Bragg's equation. The process is repeated for each face of the crystal. The lowest angle at which the maximum deflection occurs corresponds to n = 1, called Ist order reflection and so on. Generally, the angle of 1st order reflection is taken as θ in order to set the n value equal to 1.
If the θ value of the Ist order reflection from three faces viz., 100, 111 & 112 of NaCl crystal be 5.9°, 8.4° and 5.2° respectively; then from Bragg's equation, we get-
d = (nλ/2)sin−1θ
As n and λ are the same in each case,
Hence, d ∝ sin−1θ
or, d ∝ 1/sinθ
Therefore, d value in three faces are in the ratio-
d100 : d111: d112 = (1/sin 5.9) : (1/sin 8.4) : (1/sin 5.2)
or, d100 : d111: d112 = (1/0.103) : (1/0.146) : (1/0.091)
or, d100 : d111: d112 = 1.000 : 0.704 : 1.154
The ratio is closer to that exists in FCC. Hence, NaCl lattice has FCC structure of Na+ ions interlocked with similar pattern of Cl−ions.
Read also Debye–Scherrer Method X-Ray Structural Analysis of Polycrystalline and Powder Crystals
Bragg's Equation Calculator
Result:
Share
