Blanc's Rule
Blanc's Rule or Blanc Reaction
Cyclization of dicarboxylic acids on heating with acetic anhydride and then distilling at 300° or distilling directly at 300°, give either cyclic anhydrides or cyclic ketones depending on the respective positions of the two carboxyl groups.
1,4- and 1,5-dicarboxylic acids gives anhydrides while 1,6- and 1,7-dicarboxylic acids gives ketones on heating at 300°. This is called Blanc's Rule or Blanc Reaction.
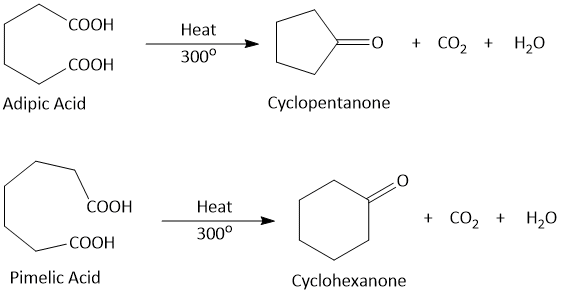
By using this rule it is possible to determine the size of rings. A double bond is introduced in the ring and the ring opened by the oxidation to the corresonding dicarboxylic acids. This is then heated with acetic anhydride and distilled. If a cyclic anhydrie is obtained, the acid is either 1,4- or 1,5-, if a cyclic ketones, the acid is either 1,6- or 1,7- and if there is no change, the acid is 1,8- or more.
