What is Alizarin? How can it synthesized?
 Alizarin is an organic compound with the chemical formula C₁₄H₈O₄. It is one of the most important mordant dyestuffs belonging to anthraquinone group. It is found in the roots of the madder plant (Rubia tinctorum) as a glycoside, ruberythric acid which on acidic or enzymatic hydrolysis gives alizarin. Alizarin forms dark red crystal. It is soluble in alkali and ethanol but sparingly soluble in water. Alizarin used to dye cotton, wool and silk fabrics. It is also used for making printing ink. Alizarin changes color depending on the pH of the solution, so it is use as a pH indicator and as a stain in biological and geological studies, particularly for detecting calcium deposits.
Alizarin is an organic compound with the chemical formula C₁₄H₈O₄. It is one of the most important mordant dyestuffs belonging to anthraquinone group. It is found in the roots of the madder plant (Rubia tinctorum) as a glycoside, ruberythric acid which on acidic or enzymatic hydrolysis gives alizarin. Alizarin forms dark red crystal. It is soluble in alkali and ethanol but sparingly soluble in water. Alizarin used to dye cotton, wool and silk fabrics. It is also used for making printing ink. Alizarin changes color depending on the pH of the solution, so it is use as a pH indicator and as a stain in biological and geological studies, particularly for detecting calcium deposits.
Synthesis of Alizarin
From Catechol
Alizarin can be synthesized by condensing phthalic anhydride and catechol in the presence of sulphuric acid at 130°C.

From Anthraquinone by Sulphonation
Anthraquinone is sulfonated with concentrated sulphuric acid at a high temperature gives anthraquinone-b-sulphonic acid which is fused with caustic soda yield alizarin.
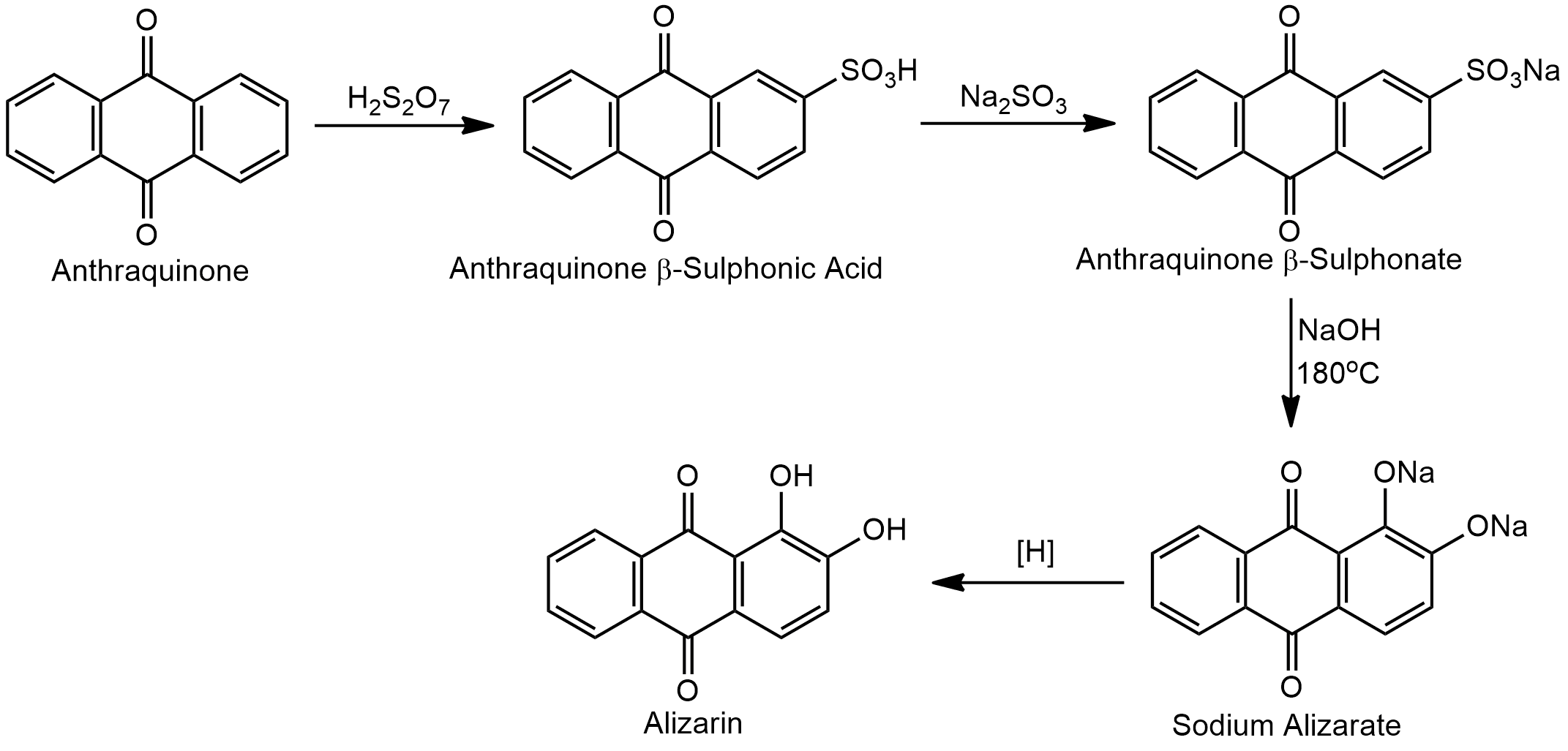
From Anthraquinone by Bromination
Alizarin can also be synthesized from anthraquinone by brominating followed by fused with caustic potash.

Read also Dyes




